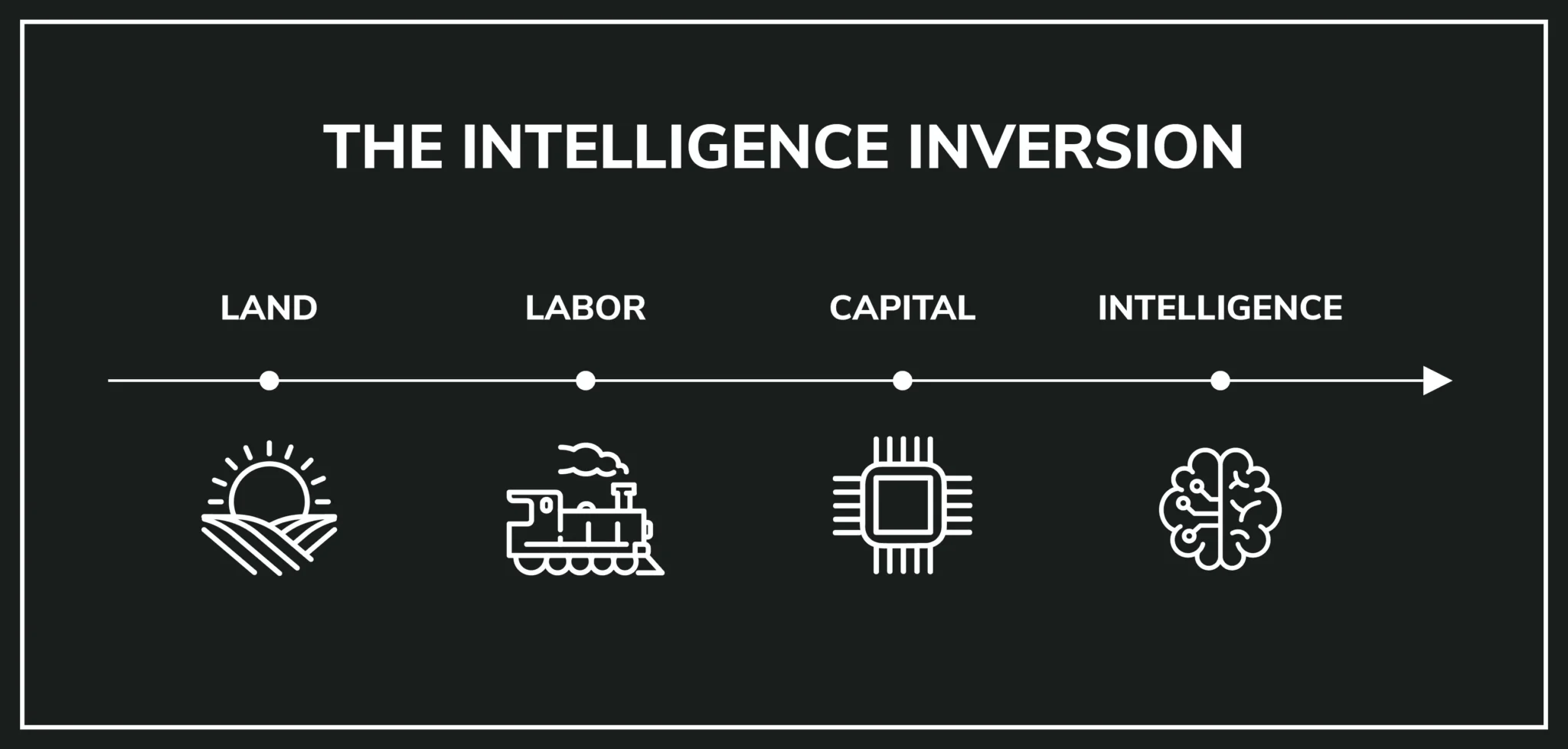
The Inversion of Intelligence in the World of AI
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, a notable shift has emerged: the inversion of intelligence. This intriguing concept suggests that as AI systems become more advanced, they may begin to mimic or enhance certain human abilities while simultaneously diminishing others. This phenomenon raises essential questions about our relationship with technology, the future of intelligence, and how we navigate this new paradigm. Understanding the implications of this inversion can help business professionals and entrepreneurs better align their strategies with the evolving AI landscape.
What Is the Inversion of Intelligence?
The term “inversion of intelligence” refers to a scenario where AI systems exhibit superior performance in specific tasks compared to their human counterparts, while also revealing weaknesses in areas traditionally held as strengths by human intelligence. For instance, AI can process massive datasets quickly and identify patterns that would take humans much longer to detect. However, this very efficiency raises concerns about the diminishing importance of critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence—qualities that are inherently human.
As companies integrate AI across sectors—from healthcare to agriculture—the conversation about intelligence inversion becomes increasingly relevant. AI tools are capable of automating complex processes, leading to a growing dependence on these systems. While the benefits are clear, including increased efficiency and reduced errors, there exists a potential downside: a loss of vital cognitive skills among the workforce.
Implications for Workforce Dynamics
One of the most pressing issues associated with the inversion of intelligence is its impact on workforce dynamics. As AI systems take over routine and repetitive tasks, employees may find themselves challenged to adapt to a new role where creativity, strategic thinking, and emotional engagement become paramount. This shift necessitates a reevaluation of workforce training and development programs.
Organizations will need to place emphasis on nurturing the uniquely human aspects of intelligence. This could involve upskilling employees to thrive in a landscape increasingly populated by AI tools. For example, developing skills in problem-solving, critical thinking, and interpersonal communication should become a top priority alongside technical proficiency.
In contrast, a failure to address this shift could lead to a workforce that is technically skilled but lacking in essential human attributes. Leaders in the business realm must understand that while AI enhances productivity, it also requires a conscious effort to maintain and develop human-centered skills.
Reassessing Human Intelligence
As AI systems continue to evolve, there is a growing need to reassess what constitutes human intelligence. Traditionally, metrics of intelligence have focused on cognitive abilities, but the rise of AI challenges this notion. How we define success and intelligence may undergo significant changes as machines excel in areas like processing and speed, which humans naturally struggle to match.
This recalibration doesn’t diminish human intelligence; instead, it suggests a redefinition. The value of human intelligence might increasingly lie in the nuances of emotional intelligence, ethical reasoning, and creative problem-solving—qualities that machines cannot replicate. This new paradigm may lead to the prioritization of skills that complement AI rather than compete with it.
Navigating AI Integration in Business
For business leaders, navigating this inversion of intelligence involves strategic foresight. As companies look to integrate AI tools, they must consider how these technologies can serve as partners rather than replacements for human intelligence. This perspective fosters a more harmonious relationship between human employees and AI systems, where each complements the other’s capabilities.
Leaders should focus on creating an organizational culture that promotes innovation and encourages employees to use AI as a complementary tool rather than solely relying on it. This could be achieved through collaborative projects where humans and AI work together to solve problems, allowing both parties to demonstrate their strengths. By adopting this approach, organizations can harness the full potential of AI while preserving and enhancing human cognitive skills.
The Ethics of AI and Human Intelligence
Furthermore, as we delve into the inversion of intelligence, ethical considerations begin to surface. The ability of AI to perform specific tasks raises questions about accountability and decision-making. As AI takes on more responsibilities, who is held accountable for its actions?
Business leaders must therefore incorporate ethical frameworks into their AI strategies. Transparency in AI algorithms and systems will ensure that human oversight remains integral, mitigating risks associated with reliance on automated decision-making. Ethics in AI development reinforces the idea that human intelligence and values should guide the deployment of AI technologies.
The Future: Embracing Greater Collaboration
In conclusion, the inversion of intelligence in AI presents both challenges and opportunities. As AI continues to advance, organizations will need to prioritize redefining human intelligence, emphasizing skills that machines cannot replicate. This will lead to a workforce that is not only technically adept but also creatively and emotionally intelligent.
As we look ahead, collaborative efforts between humans and AI systems may redefine success in the business world. Embracing this collaboration allows us to leverage the strengths of both human creativity and AI efficiency, ultimately shaping a more innovative future where intelligence—both human and artificial—thrives.
As professionals in this ever-changing landscape, keeping an eye on the implications of intelligence inversion will be crucial. Adopting strategies that nurture human skills alongside technological advancements will position leaders to not only survive but thrive in the age of AI.